Mainboard : source control circuit
The voltage stabilizer circuit on the motherboard .
3.1 – The supply voltage to components directly ( not through the voltage stabilizer )
On some motherboards and components used directly from the ATX power supply to the circuit without voltage stabilizer , which is the component :
– IC Clock gene ( Clock pulse ) using the direct source of 3.3 V
– Chipset male direct use of voltage 3.3 V , 5V and 5V STB
– IC – SiO direct use source 3.3 V and 5V STB
( The components used directly from the ATX power supply or incidents when we use poor-quality ATX )
3.1 – The supply voltage to components directly ( not through the voltage stabilizer )
On some motherboards and components used directly from the ATX power supply to the circuit without voltage stabilizer , which is the component :
– IC Clock gene ( Clock pulse ) using the direct source of 3.3 V
– Chipset male direct use of voltage 3.3 V , 5V and 5V STB
– IC – SiO direct use source 3.3 V and 5V STB
( The components used directly from the ATX power supply or incidents when we use poor-quality ATX )
3.2 – The Circuit Voltage :
– The components like CPU , RAM , Video card and chipset north they are usually run at low voltage levels so they often have their own voltage stabilizer circuit voltage from the source to 3.3V , 5V or 12V to the voltage level low from 1.3 V to 2.5 V.
– The components like CPU , RAM , Video card and chipset north they are usually run at low voltage levels so they often have their own voltage stabilizer circuit voltage from the source to 3.3V , 5V or 12V to the voltage level low from 1.3 V to 2.5 V.
a) Circuit VRM ( Vol Regu Module – Voltage Regulator Module ) : – VRM is the voltage stabilizer circuit for CPU resources , this circuit has the function to change the voltage between 1.5 V and 12 V electric current increased from about 2A to 10A to provide CPU
– On the motherboard VRM Pen3 the circuit voltage changes from 5V down to approximately 1.7 V supply for CPU
– On the motherboard VRM Pen3 the circuit voltage changes from 5V down to approximately 1.7 V supply for CPU
b ) Circuit Regu_Chipset ( voltage stabilizer circuit for the chipset )
– The supply voltage stabilizer circuit for the chipset , the Intel chipset south and north of the commonly used voltage is 1.5 V VIA Chepset often use the voltage between 3V
– The supply voltage stabilizer circuit for the chipset , the Intel chipset south and north of the commonly used voltage is 1.5 V VIA Chepset often use the voltage between 3V
c ) Circuit Regu_RAM ( voltage stabilizer circuit for RAM )
– SDRAM with bar on Pentium 3 system using 3.3 V voltage stabilizer is not required
– use Thanh DDR voltage 2.5 V , 1.8 V bar using DDR2 and DDR3 use 1.5 V bar so we need a voltage stabilizer circuit to reduce the pressure down to an appropriate voltage .
– SDRAM with bar on Pentium 3 system using 3.3 V voltage stabilizer is not required
– use Thanh DDR voltage 2.5 V , 1.8 V bar using DDR2 and DDR3 use 1.5 V bar so we need a voltage stabilizer circuit to reduce the pressure down to an appropriate voltage .
.3 – Analysis on source -level circuit diagram motherboard
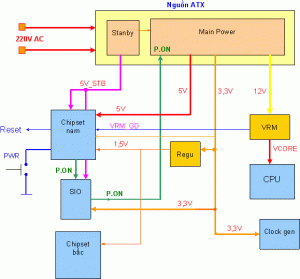
– When plugged in , the ATX power source on activities STANBY = > STB 5V supply to motherboard via the purple wire sprinkle source .
– When you press the switch = > circuit on the motherboard to boot P. ON = 0V order to control the main sources of activity , the main source of run = > to provide the motherboard voltage : 3.3 V 5V and 12V , and a secondary sources
as – 5V and – 12V
– 3.3 V Power supply directly to the IC clock pulse , male chipset , BIOS and IC – SiO – and go down through the voltage stabilizer circuit for the 1.5 V Chipset ( Intel ) or 3V finished lower level for the chipset VIA .
– Source by Circuit Voltage 12V VRM go down about 1.5 V supply voltage for the CPU
– Power supply 5V to the chipset and the PCI expansion card , reducing pressure down to 2.5 V through the voltage stabilizer circuit to power RAM
– When plugged in , the ATX power source on activities STANBY = > STB 5V supply to motherboard via the purple wire sprinkle source .
– When you press the switch = > circuit on the motherboard to boot P. ON = 0V order to control the main sources of activity , the main source of run = > to provide the motherboard voltage : 3.3 V 5V and 12V , and a secondary sources
as – 5V and – 12V
– 3.3 V Power supply directly to the IC clock pulse , male chipset , BIOS and IC – SiO – and go down through the voltage stabilizer circuit for the 1.5 V Chipset ( Intel ) or 3V finished lower level for the chipset VIA .
– Source by Circuit Voltage 12V VRM go down about 1.5 V supply voltage for the CPU
– Power supply 5V to the chipset and the PCI expansion card , reducing pressure down to 2.5 V through the voltage stabilizer circuit to power RAM
open source activities on the motherboard
Process control over resources mainboard
Process control over resources mainboard
Annotation process control source :
– When plugged in , power STANBY activities before STB 5V supply voltage for the circuit and start on male Chipset
IC – SiO
– When you switch from male chipset offers open source P. ON command , the command to the IC and then brought to the foot – SiO P. ON of power supply to motherboard Iraq ( through the Green in wireless ) to control up to Main sources Main Power activities .
– the main source of operating voltage output is :
3.3 * V – supply directly to the IC as male Chipset , SiO and Clock genes simultaneously through voltage stabilizer circuit to supply Regu
1.5 V for the two main sources Chipset
* Chipset 5V directly to the south , and granted to the PCI expansion card
* 12V supply voltage stabilizer circuit for VRM to reduce the pressure down to about 1.5 V power supply for CPU
– If the VRM circuit works well ( no problems ) it will give the source vCore (1.5 V ) supply contract for the CPU time for signal VRM_GD ( VRM_Good ) reports male chipset , this is a signal protection , if any This signal reports , understood as male Chipset CPU ready Chipset activities and gives the signal RESET to boot .
– When plugged in , power STANBY activities before STB 5V supply voltage for the circuit and start on male Chipset
IC – SiO
– When you switch from male chipset offers open source P. ON command , the command to the IC and then brought to the foot – SiO P. ON of power supply to motherboard Iraq ( through the Green in wireless ) to control up to Main sources Main Power activities .
– the main source of operating voltage output is :
3.3 * V – supply directly to the IC as male Chipset , SiO and Clock genes simultaneously through voltage stabilizer circuit to supply Regu
1.5 V for the two main sources Chipset
* Chipset 5V directly to the south , and granted to the PCI expansion card
* 12V supply voltage stabilizer circuit for VRM to reduce the pressure down to about 1.5 V power supply for CPU
– If the VRM circuit works well ( no problems ) it will give the source vCore (1.5 V ) supply contract for the CPU time for signal VRM_GD ( VRM_Good ) reports male chipset , this is a signal protection , if any This signal reports , understood as male Chipset CPU ready Chipset activities and gives the signal RESET to boot .
Notes on diagram elements
You click on the part
s diagram to see the actual circuit
You click on the part
s diagram to see the actual circuit
lqv77 discussion of :
- This is an article I own lqv77 same subject with the name “Vascular supply to the CPU on your motherboard” before collected from hocnghe.com.vn – people should refer to a different reception .
- Many people believe that blogging is not copied . My opinion that the collection or to some articles collected by topic, people share a non-profit and have quoted the source , the ” should ” .
- Depending on how people think they think I own my original intention to just collect the documents or to reference . But each time ” reading ” to register , login and again ” expensive ” and can not download the disadvantaged people too .