If some models do not install CPU power-down (such as T40), you can try to short the pins of the CPU of the remote temperature measurement method to use dummy load.
CPURST # can not only characterize the normal output voltage, the DMI-based motherboard is concerned, it can be characterized by the DMI bus connected properly, the maintenance is concerned, this can save us the measurement of DMI resistance, reducing the workload. But the motherboard does not apply Hublink architecture.
When CPURST # normal output, the focus of the next test should go into the LPC bus, because the CPU wants to read the BIOS, LPC is a necessary channel. The FSB, DMI (Hublink) as too fast, useful information can not be obtained through the oscilloscope.
In general, if the LPC moment no action, the focus should be placed in the CPU test working conditions. If there is an instant action, the focus should be placed north and south bridge test, EC and BIOS above, of course, including LPC’s own resistance to the ground.
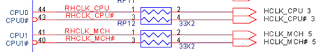
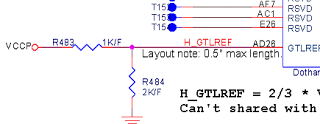
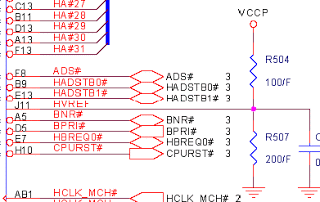
The CPU test points, in addition to the foregoing CPURST and CPUPWRGD, as well as test points to be measured:
Negative output power supply may also affect the CPU to the CPU’s normal to go yard. Although the CPU power supply has output, but the CPU is a high-speed devices, sensitive to external conditions, have the CPU power supply output is still necessary to look at the power supply waveform.
It should be clear that the majority take the FF machine, we could not measure the voltage on any surface and waveform abnormalities, the more new models more so. Many cases can only be tentative brush BIOS or change the bridge. General order for the bridge is Southbridge, Northbridge, CPU. In terms of models for Hublink architecture, PCI bus exception will lead to not go yard. If the bus between the Northbridge and Southbridge conditions have Hublink amount again. After DMI architecture models, there is no CPURST enough to reflect the DMI bus connections, no need to measure.